Safeguarding your business from cyber threats is incredibly important. As technology becomes more central to our operations and data keeps growing rapidly, the danger of falling victim to cybercriminals is on the rise. This article will explore the top 10 cybersecurity threats that businesses commonly face and provide recommendations on how to defend your business against them.
Cybersecurity isn't just about IT — it's a serious business concern with far-reaching consequences. A successful cyberattack can result in financial loss, damaging your reputation, and even legal issues. It can interrupt your work, reveal important information, and make customers lose faith in you. This is why investing in cybersecurity isn't just a good idea, but a necessary one to safeguard your business and everyone involved.
Common Types of Cybersecurity Threats
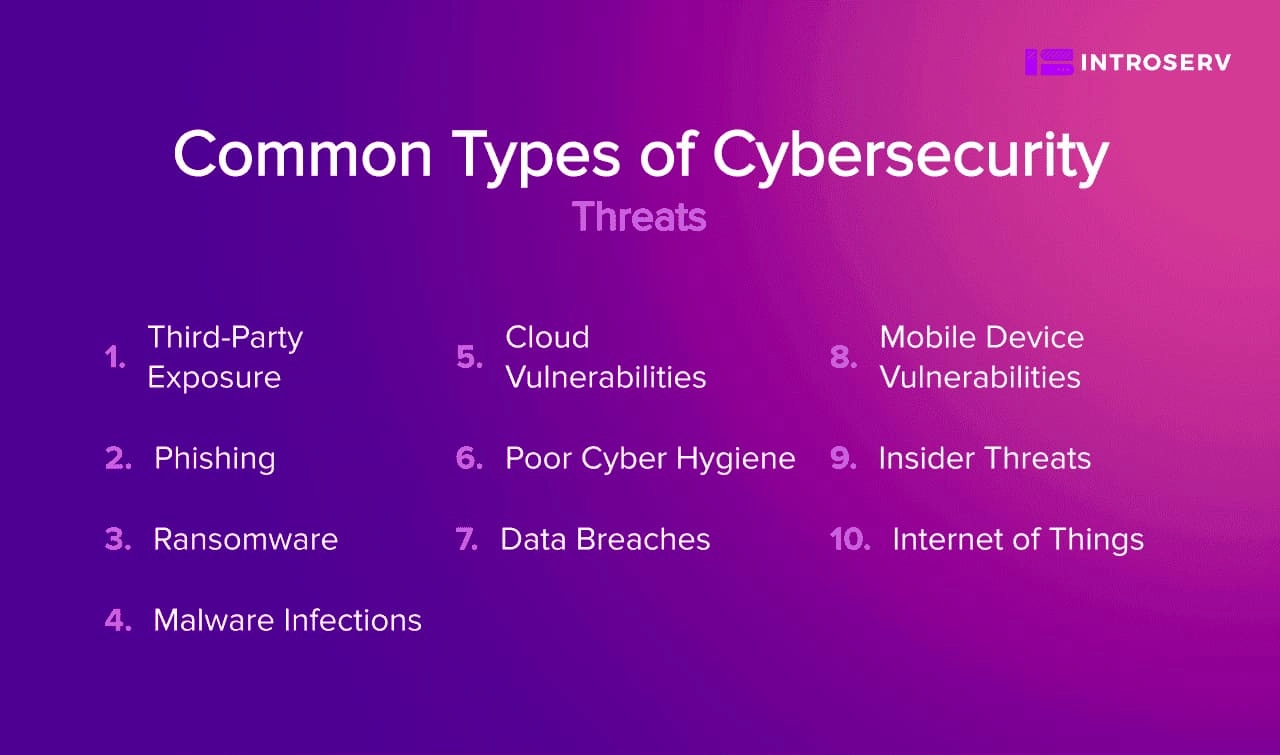
1. Phishing
Phishing remains a widespread and sneaky threat to businesses. It uses psychology to trick individuals into sharing sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card details. Phishing often involves emails, messages, or websites that pretend to be trustworthy sources like banks or government agencies.
Attackers aim to create a sense of urgency, pushing recipients to act quickly. They create messages that ask for personal information, password changes, or financial transactions. These tricky emails copy official communication, making recipients lower their guard. The promise of rewards entices people to click on links or download files hastily.
To shield your business from phishing, follow these key steps:
- Teach your employees how to spot phishing emails and suspicious links.
- Use strong email filters and software that spots spam.
- Add extra security by using two-factor authentication for all accounts.
- Keep your software up to date and fix any issues to stop cybercriminals from taking advantage of weaknesses.
2. Ransomware
Ransomware stands as a malicious software crafted to breach a system, lock away vital data, and demand payment for its release. Typically, these assaults kick off innocuously through email attachments, suspicious links, or compromised sites. Once set in motion, the malware races through networks, encrypting files and denying user access. Cybercriminals then demand for payment, often in cryptocurrency, to furnish the decryption key required to reclaim data access. The urgency of the situation coerces victims into paying, hoping to reestablish business flow.
The aftermath of a ransomware attack can be dire. Businesses could grapple with prolonged downtime, resulting in revenue and productivity losses. Moreover, the potential exposure of sensitive customer data might trigger legal repercussions and undermine trust among clients and partners. Yet, paying the ransom isn't a guaranteed fix; some attackers might not hold their end, leaving businesses vulnerable to cyber threats.
To defend against ransomware attacks, implement the following best practices:
- Consistently back up essential data and store it in a secure cloud setting or offline.
- Maintain software and operating systems up to date to tackle potential vulnerabilities.
- Educate employees to exercise care when handling dubious email attachments or unfamiliar links.
- Implement strong firewall and intrusion detection systems to detect and thwart ransomware attacks.
3. Malware Infections
Malware poses a significant threat to businesses. Malware is short for malicious software, and it includes all sorts of malicious code meant to infiltrate, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems.
Malware appears in diverse forms, including viruses, worms, trojans, and spyware, each carrying its own distinct traits and capabilities. These threads often take advantage of weak spots in software or how people act with computers. People might not even know they're downloading and using malware when they click on links or get what seems like harmless files.
Malware infections can arise through an array of pathways, spanning from infected email attachments to compromised websites. Once it's inside, malware can mess up data, interrupt operations, and grant unauthorized access to cybercriminals.
To protect your business from malware attacks, consider the following measures:
- Install trusted antivirus and anti-malware solutions on all devices.
- Perform frequent system scans for malicious software and ensure timely updates.
- Steer clear of downloading content or applications from unreliable origins.
- Promote employee vigilance while interacting with unfamiliar links or attachments.
4. Poor Cyber Hygiene
Neglecting basic security practices can lead to poor cyber hygiene, which makes it easier for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities and breach digital defenses. This includes a variety of practices that may not seem harmful individually, but when combined, weaken the security of your computer system. Failing to update software regularly, ignoring password guidelines, and underestimating the importance of cybersecurity training can create an ideal environment for cyberattacks.
To promote good cyber hygiene within your organization, consider the following recommendations:
- Implement strict password rules, which involve frequent password updates and the use of unique, complex passwords.
- Arrange routine cybersecurity sessions to educate employees about best practices and the significance of maintaining good cyber hygiene.
- Ensure all software and systems are current with the newest security fixes and updates.
- Regularly carry out security evaluations and vulnerability assessments to pinpoint and rectify any flaws in your online security setup.
5. Data Breaches
No thread presents a larger threat to businesses and their customers than data breaches. These breaches, often the result of complex cyberattacks, can not only expose private information, but also corrode the bedrock of customer trust upon which businesses depend.
The consequences of a data breach can impact a business in many ways, causing lasting harm:
- Harm to Reputation: The loss of customer data due to a breach can stain a business's reputation. The safeguarding of personal information holds immense importance for customers, and a breach can chip away at trust, possibly causing a loss of customers.
- Legal Consequences: In a time of strict data privacy rules like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), businesses can face serious legal actions and financial penalties for not properly securing customer data.
To shield your business from data breaches, take these forward-looking measures:
- Set up strong access controls and encryption methods to protect sensitive data.
- Regularly monitor and trace user actions to find any suspicious or unauthorized access attempts.
- Create plans for responding to incidents to ensure a quick and effective reaction if a data breach occurs.
- Carry out routine security checks and tests to pinpoint and fix any weaknesses in your systems.
6. Third-Party Exposure
The growing reliance on external partners and vendors has become vital for progress and effectiveness. However, this dependence also brings a possible vulnerability: exposure through third parties.
External partners and vendors might unintentionally provide an opening for cyber threats. If their systems and procedures aren't properly protected, they could serve as entry points for attackers. This issue isn't just a theoretical vulnerability; it has tangible consequences:
- Cascade of Weakness: Much like a chain being only as strong as its weakest link, a business's cybersecurity is only as strong as the security measures of its third-party collaborators. A vulnerability in any one of these collaborators can spread weaknesses across the entire network.
- Impact on Continuous Operations: A security breach originating from a third-party vendor can interrupt your activities, leading to downtime, harm to reputation, and financial setbacks.
To reduce the risks tied to third-party exposure, consider these actions:
- Perform thorough research when choosing third-party vendors, assessing their cybersecurity methods and rules.
- Create clear written agreements that detail responsibilities and expectations related to cybersecurity.
- Regularly evaluate the cybersecurity stance of third-party vendors through audits and assessments of vulnerabilities.
- Supervise third-party entry and actions within your systems to identify any suspicious conduct.
7. Insider Threats
Though external dangers often grab the spotlight, insider threats can be equally harmful to businesses. An insider threat refers to a present or past employee, contractor, or business ally who purposely or accidentally endangers your organization's security.
Insider threats take on different forms, presenting various difficulties for businesses:
- Harmful Intent: At times, a worker with harmful intentions can act as a concealed saboteur. Dissatisfied workers or those chasing financial benefit might exploit their familiarity with the organization's systems to breach security.
- Unintended Breaches: Not every insider threat stems from ill will. Innocent errors, like clicking on a harmful link or mishandling sensitive information, can mistakenly lay bare an organization to cyber dangers.
To effectively tackle insider threats, implement these approaches:
- Enforce stringent access controls and permissions based on roles to restrict sensitive information access.
- Nurture a culture of awareness about cybersecurity and offer regular training to staff about guarding data and the dangers of insider threats.
- Regularly track and audit user actions to identify any strange behavior or unauthorized entry attempts.
- Encourage staff to swiftly report any dubious conduct or possible insider threats.
8. Internet of Things
IoT, short for the Internet of Things, describes the network of devices, objects, and systems equipped with sensors, software, and connectivity to collect and exchange data. From smart thermostats and wearables to industrial machinery, IoT has integrated into various facets of modern life. The widespread connection brings new challenges. Every IoT device can be a potential entry point for hackers seeking unauthorized access to corporate networks or sensitive data.
The surge in IoT devices often brings along lax security, heightening the risk of exploitation:
- Feeble Security Standards: Many IoT devices lack sturdy security features. Default passwords, weak encryption, and insufficient software updates provide fertile ground for cybercriminals.
- Diverse Ecosystem: The IoT environment spans various devices, each with different security levels. This diversity makes it tough to establish consistent security protocols.
To bolster IoT security within your company, consider these suggestions:
- Change the default usernames and passwords on IoT devices and use strong, distinct credentials.
- Keep updating IoT device software regularly to fix any recognized vulnerabilities.
- Divide your network to separate IoT gadgets from vital business systems.
- Implement network monitoring and anomaly detection to notice any suspicious behavior linked to IoT devices.
9. Mobile Device Vulnerabilities
Smartphones and tablets play a pivotal role in business tasks, helping employees to stay productive on the go. However, vulnerabilities in mobile devices could potentially put an organization's security and private data at risk.
Attackers exploit the distinctive weaknesses of mobile devices to infiltrate networks and steal valuable data:
- Operating System Weak Points: Outdated operating systems often carry unpatched security vulnerabilities that attackers can take advantage of.
- Phishing Campaigns: Phishing tactics extend beyond emails. Attackers might dispatch malevolent links via text messages or social media apps, deceiving users into divulging sensitive information.
- Unsecured Wi-Fi Connections: Public Wi-Fi networks are infamous for their lack of security, exposing devices to potential eavesdropping and data interception.
- Malicious Applications: Attackers might create seemingly authentic mobile apps embedded with malware. Once installed, these apps can illicitly access sensitive data.
To safeguard your business from mobile device vulnerabilities, the following effective steps:
- Enforce robust authentication methods like biometric or multi-factor authentication to fortify mobile devices.
- Encrypt all confidential data stored on mobile devices to block unauthorized access.
- Regularly update mobile device operating systems and apps to mend known security gaps.
- Educate workers about the risks linked to downloading apps from unreliable sources and clicking on dubious links.
10. Cloud Vulnerabilities

The embrace of cloud computing brings a wealth of advantages, like scalability, worldwide accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, these benefits walk alongside potential security risks:
- Flawed Access Management: Incorrectly set access controls might allow unauthorized parties to reach vital data and applications.
- Unshielded Data: Keeping unencrypted data in the cloud exposes it to potential interception and compromise.
- Data Breaches: If proper security measures are lacking, sensitive cloud-stored data becomes vulnerable, risking data breaches that undermine customer trust and brand standing.
- Misconfigured Cloud Settings: Cloud platforms provide a spectrum of settings. Misconfigurations can accidentally reveal data to the public internet or grant unauthorized access to resources.
To boost your cloud security, ponder these tactics:
- Pick trustworthy cloud service providers that offer strong security measures and compliance confirmations.
- Implement robust access controls and identity management protocols to prevent unauthorized entry to cloud resources.
- Regularly monitor and audit cloud environments to uncover suspicious activity or potential weak spots.
- Encrypt sensitive cloud-stored data to ensure its confidentiality and integrity.
Conclusion
Shielding your business from cybersecurity threats requires a forward-thinking and comprehensive approach. By comprehending the particular dangers that businesses confront, training your team, and establishing strong security measures, you can significantly lessen the chances of becoming a victim to cybercriminals.
Investing in cybersecurity isn't just a necessary cost; it's an input in the long-term viability and success of your business. By giving prominence to cybersecurity, you can safeguard private data, maintain customer confidence, and protect your organization from financial and reputational damage.