What is Remote Access and How Does It Work?
Remote access refers to the ability to connect to and control a computer or network from a remote location. With remote access, you can reach files and programs from anywhere in the world, as long as you have an internet connection.
Remote access works by making a connection between your device and the computer or network you want to reach. Usually, special software or VPN (Virtual Private Network) tech helps create this connection. When you start a remote access session, your device asks the target computer or network for permission, and once granted, you get access. This connection allows you to control the remote device as if you were physically present, so you can do tasks and reach resources from a distance.
Why Do We Need Secure Remote Access?
The need for safe remote access is important for many groups, like students, individuals, and organizations of all sizes. Here's why reliable remote access matters for each of them:
- Students: Secure remote access lets students attend online classes, work on projects together, and use educational stuff without worrying about their data or privacy.
- Professionals: Employees benefit from dependable remote access because it allows them to switch smoothly between work and personal stuff while safeguarding vital information.
- Organizations: In the business world, robust remote access is a must-have. It guarantees that employees can work remotely without exposing sensitive company data. This way, productivity stays high, and data stays secure.
Benefits of Remote Access
Remote access brings numerous advantages for both individuals and organizations. The key benefits include:
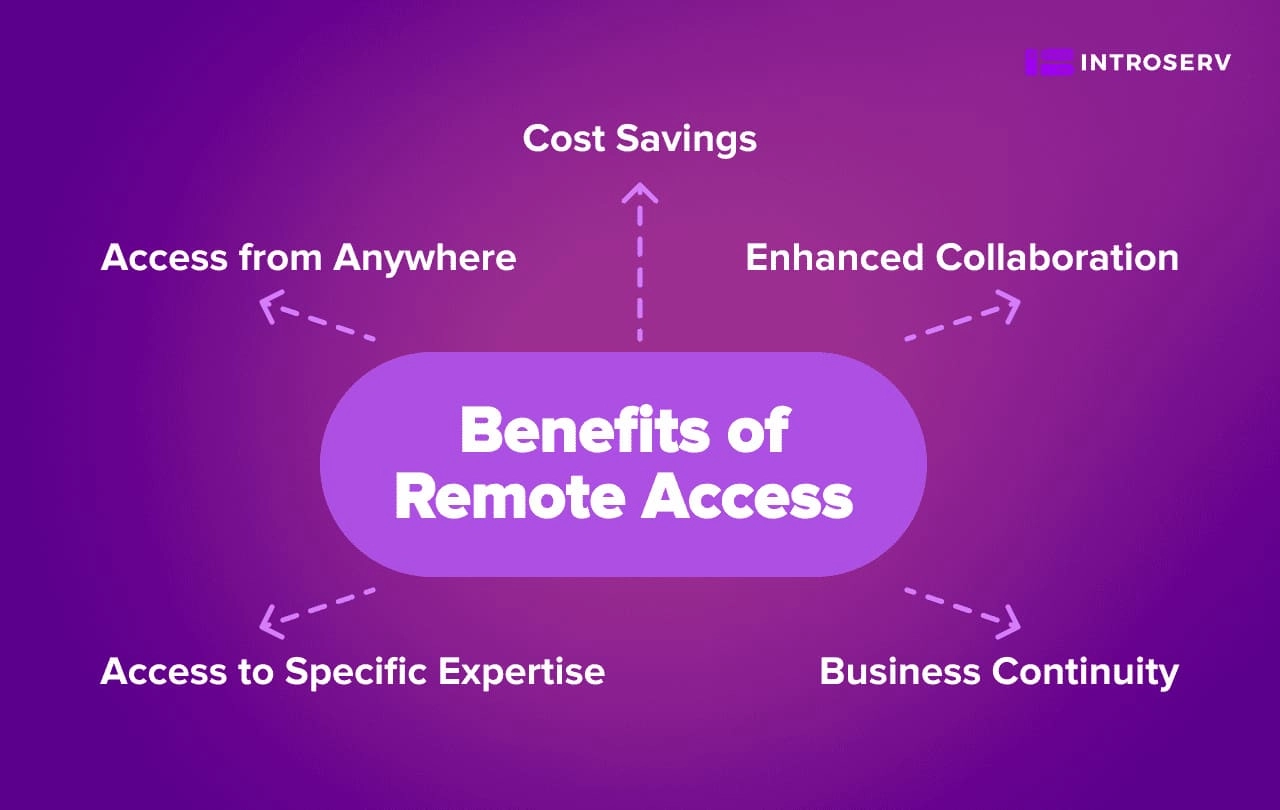
- Access from Anywhere: Remote access lets you work from any place you choose, offering the freedom to pick your location and work at your own pace. This flexibility can significantly improve your work-life balance and productivity.
- Cost Savings: Organizations can cut costs by not needing a dedicated office space, reducing expenses for both individuals and businesses. Remote access also trims commuting costs and allows for more efficient use of resources.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Remote access allows teams to collaborate effectively, even if they are spread out across different locations. Tools like video conferencing and shared document repositories make communication and collaboration seamless.
- Business Continuity: Even during emergencies or natural disasters, remote access enables the management of critical systems and data. This capability is vital for ensuring business continuity and minimizing downtime.
- Access to Specific Expertise: Remote access allows individuals and organizations to tap into specialized resources, expertise, and talent from anywhere in the world.
Types of Remote Access Solutions
There are several variants of remote access solutions available, each with its own security implications. Here are some commonly used methods:
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
VPNs are widely used to create secure connections between remote users and corporate networks. They build an encrypted tunnel through which data travels to keep it private and intact. VPNs are a good choice when security and data protection are paramount, especially for accessing sensitive resources and applications.
Limitations:
- Setting up a VPN can be complex for non-technical users.
- High data traffic may occasionally result in reduced network performance.
- Scaling a VPN infrastructure for a large number of users can be technically and logistically challenging.
Remote Desktop Services
RDS (Remote Desktop Services) is a Microsoft technology developed with a primary focus on business and enterprise applications. It is designed to enable multiple users to access a remote desktop session on a Windows Server. This solution is commonly used for technical support, collaboration, and accessing files and applications on a remote system.
Limitations:
- It is primarily designed for Windows environments, limiting compatibility with other operating systems.
- It can be resource-intensive, demanding robust server hardware.
- Administrators need to manage user access and applications on the remote desktop server.
Cloud-Based Access Solutions
Cloud-based solutions, like Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), provide remote access to files, applications, and resources stored in the cloud. These approaches offer centralized security controls, scalability, and the ability to leverage cloud infrastructure for secure access. Cloud-based solutions, especially VDI, often have minor limitations that can be addressed by the service provider, making them a highly versatile and adaptable option for remote access.
Limitations:
- Access relies on a stable internet connection.
- Costs can accumulate over time, particularly in larger deployments.
- Integrating your existing on-premises systems with cloud solutions can be a complex process that demands careful planning and implementation.
Remote Access Software
Remote access software is not a primary remote access solution like VPNs, RDS or Cloud-based access. It includes tools like TeamViewer, AnyDesk, and others. The program enables users to connect to and control other computers or devices over the internet. This approach is typically used for remote support and administration.
Limitations:
- Incorrectly configured software can pose security risks.
- Performance may vary depending on internet connection quality.
- Compatibility issues may arise when connecting to different operating systems and device types.
In terms of safeguarding remote access, Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) emerges as one of the most secure options. With VDI, no critical data is stored on local devices. It creates isolated and controlled desktop instances on a centralized server and keeps sensitive information within the controlled environment.
This approach significantly reduces the risk of data leaks or losses due to device theft or compromise. It enables businesses to establish strict access controls, monitor user activities, and conduct regular security audits. We recommend VDI for organizations that prioritize data security and seek a scalable and efficient remote work experience.
Best Practices for Secure Remote Access

Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication eliminates the need for traditional passwords. It boosts security, cuts down on the costs linked to password management, and lowers the chances of password-related security problems.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA remains a key part of secure remote access. Utilize MFA solutions that require two or more authentication factors, such as knowledge-based, possession-based, or entity-based methods. MFA improves security by adding an extra layer of validation, making it much harder for unauthorized access.
Access Control
By implementing granular control over access, you can establish access control policies that align with the principle of least privilege. This guarantees that individuals only have access to resources necessary for their roles. Robust access control mechanisms restrict unauthorized entry and safeguard sensitive information.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM solutions are vital for handling user identities, roles, and permissions. They enable organizations to verify user identities, control access, and enforce authentication and authorization policies. IAM plays a pivotal role in securing remote access by ensuring that only authorized users gain entry to critical resources.
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
PAM tools and technologies help secure, monitor, and control access to privileged accounts within an organization. Continuously monitor privileged access to detect and respond to unusual network activity, reducing the risk of unauthorized network access. However, bear in mind that PAM management can be time-intensive, and privileged credential abuse remains a common target for cyberattacks.
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
If your organization utilizes RDP for remote access, ensure it is configured securely. Implement strong encryption, disable unnecessary features, and apply stringent access controls. Regularly patch and monitor RDP to prevent vulnerabilities that may compromise your internal network.
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
As employees bring their own devices to the workplace, it's essential to create comprehensive BYOD security policies and procedures. These guidelines should encompass centralized device management, staff training, and strict security guidelines. Address concerns such as data loss, unauthorized access, malware infections, compliance, and device management.
Risk-Based Authentication
Employ risk-based authentication to assess the risk level of each access attempt in real-time. Factors considered may include login time and location. Based on risk scores, apply appropriate levels of verification, enhancing security while minimizing user friction.
Zero Trust
Zero Trust mandates secure, authenticated, and authorized access to resources, irrespective of a user's status within the organization. Implement the least privilege principle to limit access to resources to only those required for specific tasks. By adopting Zero Trust principles, your organization enhances its security posture and readiness to defend against sophisticated attacks.
Unlock the Potential of Secure Remote Access with INTROSERV
INTROSERV streamlines secure access control. Through virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), you can establish a centralized and secure gateway for employee access from any internet-connected device. Our approach integrates robust security features such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and centralized management.
With our comprehensive secure remote access solutions, you can empower your workforce, boost productivity, and fortify data protection against unauthorized access. Contact us today to explore how INTROSERV can elevate your secure remote access strategy.